Overview of 3D Printing Powder Spherical Tantalum Powder Nb Mo Ta Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Metal powder is a common form of metal that has been processed into fine particles, ranging from a few micrometers to over 100 microns in diameter. It plays a crucial role in various industrial applications due to its unique properties and versatility.
Features of 3D Printing Powder Spherical Tantalum Powder Nb Mo Ta Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Physical Characteristics
Particle Size: Ranging from nanometers to hundreds of micrometers, the size distribution significantly influences the powder’s flowability, packing density, and sintering behavior.
Shape: Particles can be spherical, irregular, flake-like, or dendritic, each shape affecting the final product’s mechanical properties and surface finish.
Purity: Depending on the production method, metal powders can achieve high levels of purity, critical for applications like electronics and aerospace where impurities can degrade performance.
Density: While less dense than their solid counterparts due to the presence of air between particles, metal powders can be densely packed during processing to approach the density of the solid metal.
Chemical Properties
Reactivity: Some metal powders, particularly aluminum and titanium, are highly reactive with air and moisture, necessitating careful handling and storage under inert atmospheres or vacuum.
Oxidation: Exposure to air can lead to surface oxidation, forming a passive layer that affects sintering and other processes. This can be managed through surface treatment or use of protective atmospheres.

(3D Printing Powder Spherical Tantalum Powder Nb Mo Ta Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing)
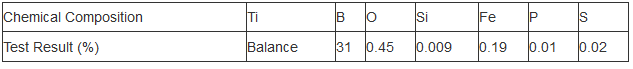
Parameters of 3D Printing Powder Spherical Tantalum Powder Nb Mo Ta Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Title: High-Quality Spherical Tantalum, Nb, Mo, and Ta Metal Powders for 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction:
The advent of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has revolutionized the way we create complex geometries and intricate components across various industries. Among the numerous materials available for this process, spherical tantalum (Ta), niobium (Nb), molybdenum (Mo), and tantalum metal powders hold significant promise due to their unique properties. This article delves into the key parameters of these powders, specifically tailored for additive manufacturing applications.
1. Particle Size Distribution:
Spherical tantalum, Nb, Mo, and Ta powders exhibit a narrow particle size distribution, typically ranging from 10 to 63 microns. This homogeneity is crucial for achieving consistent layer adhesion and print resolution in 3D printed parts. A narrow PSD ensures better flowability during the printing process and reduces the risk of defects.
2. Shape and Sphericity:
The spherical shape of these powders offers several advantages. They provide a higher surface area-to-volume ratio, enhancing reactivity and reducing the required energy input during melting. The uniform shape also contributes to more efficient use of material, as it minimizes powder settling during storage and reduces the need for post-processing.
3. Chemical Purity:
High purity spherical tantalum, Nb, Mo, and Ta powders are essential for achieving accurate material properties in the final product. Purities above 99.9% are commonly sought after to minimize impurities that could affect mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and other critical performance characteristics.
4. Melting Point and Thermal Conductivity:
Tantalum, niobium, molybdenum, and tantalum have high melting points that make them suitable for demanding applications. Tantalum’s melting point is around 3017°C, while Nb, Mo, and Ta are approximately 2995°C, 2623°C, and 3380°C, respectively. These metals’ excellent thermal conductivity ensures efficient heat transfer during the printing process, which is vital for maintaining print quality.
5. Mechanical Properties:
The combination of strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance makes these metals ideal for 3D printing. Tantalum possesses high strength and excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for aerospace and medical applications. Niobium and molybdenum offer good mechanical properties and can be used in stress-bearing components, while tantalum’s unique combination of strength and stability makes it popular in high-temperature applications.
6. Printability and Adhesion:
The powders’ spherical shape, along with their inherent surface characteristics, facilitates better flow and improved adhesion to the build platform. This results in fewer support structures and reduced post-processing requirements, ultimately saving time and resources.
7. Environmental Considerations:
Sustainable sourcing and minimal environmental impact are increasingly important in the 3D printing industry. Tantalum, niobium, molybdenum, and tantalum powders should be sourced responsibly, with considerations for recycling and waste management practices.
Conclusion:
In summary, spherical tantalum, Nb, Mo, and Ta metal powders are highly sought-after for their exceptional properties and compatibility with 3D printing processes. Their precise particle size distribution, spherical shape, chemical purity, and thermal characteristics make them ideal for a wide range of applications. As additive manufacturing continues to evolve, the optimization of these powders will play a pivotal role in pushing the boundaries of what is possible in terms of material choice and design complexity.

(3D Printing Powder Spherical Tantalum Powder Nb Mo Ta Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing)
FAQs of 3D Printing Powder Spherical Tantalum Powder Nb Mo Ta Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing
Inquiry us